|
|
|
|
News The Project Technology RoboSpatium Contribute Subject index Download Responses Games Gadgets Contact <<< Chemical equation Electrolysis >>> Redox reactionOxidationThe French chemist Antoine Laurent de Lavoisier constituted the concept of oxidation to describe chemical compounds containing the element oxygen. He demonstrated the role of oxygen in the rusting of metal and showed that respiration was essentially a slow combustion of organic material using inhaled oxygen.Some later the term oxidation was extended to reactions in which hydrogen is extracted from a molecule. Based on modern theories about the composition of electron shells, the chemical process of oxidation was generalized. Nowadays oxidation is defined as the loss of electrons or the increase in oxidation state by a molecule, atom or ion. Oxidation stateThe oxidation state is an indicator of the degree of oxidation of an atom in a substance. To determine those degree of oxidation, some rules have to be followed:1.) The oxidation state of a free, uncombined element is zero. 2.) The oxidation state of a free monoatomic ion is equal to the net charge on the ion. For example sodium chloride is an ionic compound with the formula NaCl. The oxidation state of the positively charged sodium cation is +1, those of the negatively charged chloride anion is -1. The twice positively charged magnesium cation of magnesium chloride (MgCl2) has the oxidation state of +2, while the two negatively charged chloride anions have the oxidation state of -1. 3.) Electron pairs of covalent bonds are assigned to the atom with the higher value of electronegativity. For this reason hypothetical ions are formed and according to rule number two, the oxidation state is equal to the hypothetical charge. Let's determine rule number three with the help of some examples: 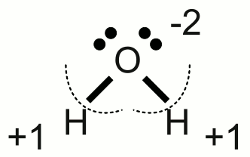 Water molecule:
Water molecule:A water molecule consists of one oxygen atom forming two covalent bonds with two hydrogen atoms. The electronegativity of oxygen is higher than those of hydrogen (referring to the PTE table), hence the electron pairs of the covalent bonds are assigned to the oxygen atom which features (virtually) by now eight valence electrons. A elemental oxygen atom has six valence electrons and so the virtual oxygen ion of the water molecule is twice negatively charged. The oxidation state of the oxygen atom in a water molecule is -2. Each hydrogen atom has (virtually) lost it's valence electron forming a single charged cation with what the oxidation state of each hydrogen atom in the water molecule is +1. 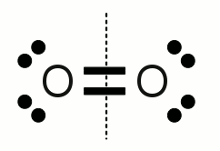 Oxygen molecule:
Oxygen molecule:An oxygen molecule consists of two oxygen atoms forming a double bond. The electronegativity of both atoms has the same value. For this reason the electron pairs of the double bond are split equally to both atoms. The number of valence electrons of each oxygen atom equals six, which is the number of an isolated neutral oxygen atom, hence the oxidation state is zero. That's the confirmation of rule number 1. 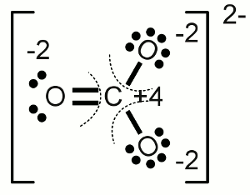 Carbonate anion:
Carbonate anion:The electronegativity of oxygen is higher than those of carbon, hence the electron pairs of the covalent bonds are assigned to the oxygen atoms. One of the oxygen atoms forms a double bond with the carbon atom at the center of the molecule, each of the two other oxygen atoms forms a single bond with the carbon atom. Another characteristic of the carbonate ion is the fact that it is twice negatively charged. Those supernumerous electrons are allocated to the two oxygen atoms forming a single bond with the carbon atom. As a result we get an oxidation state of -2 for the three oxygen atoms and an oxidation state of +4 for the carbon atom which has "lost" all of it's valence electrons. The sum of the values of all oxidation states equals -2 ReductionThe process of reduction is the reversal process of oxidation, hence it is the gain of electrons respectively the decrease of the oxidation state.RedoxWhenever one or more atoms become oxidized during the process of a chemical reaction, one or more atoms have to become reduced at the same process. The term redox reaction (shorthand for reduction-oxidation) describes chemical processes in which the oxidation state of atoms is changed.Substances reducing other substances are said to be reductive or reducing and are known as reducing agents, reductants or reducers. On the other hand substances oxidizing other substances are called to be oxidative or oxidizing and are known as oxidizing agents, oxidants, or oxidizers. Reductans transfer electrons to another substance, thus they get oxidized themselves. Vice versa oxidants remove electrons from another substance and get reduced themselves. Reductans are also called electron donors because they "donate" electrons. Accordingly oxidants are called electron acceptors because of the fact that they "accept" electrons. The sum of (virtually) transferred electrons is zero, meaning no electrons are lost or created during a redox reaction. Examples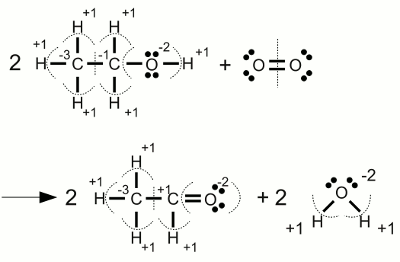 Oxidation of ethanol (alcohol) to acetaldehyde:
Oxidation of ethanol (alcohol) to acetaldehyde:The oxidation state of the two carbon atoms inside the ethanol molecule differs. During the reaction with oxygen, the right carbon atom changes it's oxidation state from -1 to +1, hence it (virtually) looses two electrons. The oxidation state of the elementary oxygen is zero. During the chemical reaction with two hydrogen atoms of the ethanol, resulting in water molecules, each molecular oxygen atom is gaining two electrons and changes it's oxidation state from zero to -2. When looking at the stoichiometric numbers, we can see that two ethanol molecules on the left side yield two acetaldehyde molecules on the right side, meaning one carbon atom of each ethanol molecule looses 2 electrons. Vice versa one oxygen molecule, consisting of two oxygen atoms, yields two water molecules, meaning each of the two oxygen atoms gain two electrons. The oxygen molecule acts like an oxidant, thus it is itself reduced. Vice versa ethanol acts like a reductant, thus it is itself oxidized. 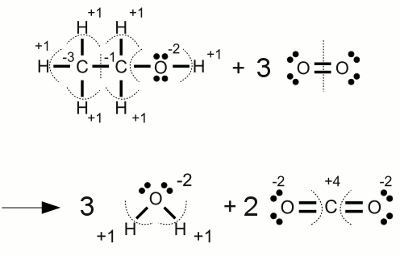 Combustion of alcohol:
Combustion of alcohol:The complete combustion of ethanol forms water and carbon dioxide. During this process the carbon atoms change their oxidation state from -3 respectively -1 to +4 (the highest oxidation state possible for carbon). The oxidation state of the participating elementary oxygen atoms are changing from zero to -2. <<< Chemical equation Electrolysis >>> News The Project Technology RoboSpatium Contribute Subject index Archives Download Responses Games Links Gadgets Contact Imprint |
|
|